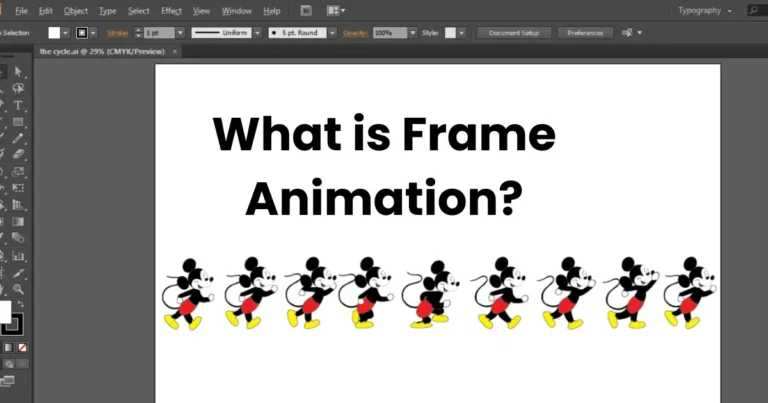
How to make 3D animation? | best guide for beginners to make animation

Contents
- 1 Animation Pipeline: How to make 3D animation?
- 2 Tools and Software for 3D Animation
- 3 Step-by-Step Guide: How to make 3D animation?
- 4 Tips for Beginners in 3D Animation
- 5 Challenges in 3D Animation and How to Overcome Them
- 6 Applications of 3D Animation
- 6.1 1. Entertainment
- 6.2 2. Marketing and Advertising
- 6.3 3. Architecture and Real Estate
- 6.4 4. Education and Training
- 6.5 5. Healthcare and Medicine
- 6.6 6. Manufacturing and Engineering
- 6.7 7. Science and Research
- 6.8 8. Retail and E-Commerce
- 6.9 9. Automotive and Aerospace Industries
- 6.10 10. Social Media and Content Creation
- 6.11 Future Applications
- 6.12 Conclusion
We know that if you are passionate about making 3D videos you always try to find the answer to this question of how to make 3D animation and which steps you should follow to make a stunning 3D video but you need not worry about these questions anymore because we are here with a complete guide to make 3D animation.
3D animation is the art of bringing digital objects to life in a three-dimensional space, allowing them to move and interact as though they exist in the real world. Unlike traditional 2D animation, where images are drawn and animated on a flat plane, 3D animation creates depth, realism, and a sense of immersion that captivates audiences across industries.
In today’s digital age, 3D animation and graphic design play a pivotal role in entertainment, marketing, education, and more. From blockbuster movies and video games to medical simulations and product advertisements, its applications are vast and ever-growing. For creators, 3D animation is not just a tool—it’s a medium to tell stories, visualize concepts, and push the boundaries of imagination.
This guide will explore the ways how to make 3D animation and the fascinating world of 3D animation with its processes, tools, and techniques while offering insights for both beginners and seasoned professionals. Whether you’re drawn to the cinematic allure of animated films or the technical challenges of creating lifelike environments, the journey into 3D animation promises to be as exciting as it is rewarding.
Animation Pipeline: How to make 3D animation?
The 3D animation pipeline is the structured sequence of steps followed to create a 3D animation project, from the initial concept to the final polished output. This systematic approach ensures that every element, from modeling to rendering, comes together seamlessly. Below is an overview of the key stages in the 3D animation pipeline:
1. Pre-Production
This is the planning phase, where the foundation of the animation project is laid out.
- Concept Development: Brainstorming ideas and creating a clear vision for the animation.
- Scriptwriting: Crafting a script to outline the story or sequence of events.
- Storyboarding: Sketching scenes to visualize how the animation will flow.
- Animatics: Creating a rough, animated version of the storyboard to plan timing and pacing.
2. Production
The production phase involves creating the visual and functional elements of the animation.
- Modeling:
Artists build 3D models of characters, props, and environments using software like Blender or Maya. These models serve as the building blocks of the animation. - Texturing:
Textures and materials are applied to models to give them a realistic appearance, such as skin, fabric, or metal. - Rigging:
A digital skeleton is added to models, allowing them to be posed and animated. Rigging includes setting up joints, bones, and controls for movement. - Animation:
Characters and objects are brought to life using keyframes, timelines, and motion capture techniques. This stage defines how elements move and interact. - Lighting:
Lighting is added to enhance mood, realism, and depth. Virtual lights simulate real-world lighting conditions. - Rendering:
The 3D scene is converted into a 2D image or video format. Rendering combines all visual elements, including textures, lighting, and animation, into the final output.
3. Post-Production
In this final stage, the rendered animation is polished and prepared for distribution.
- Compositing:
Multiple rendered layers are combined into a single cohesive scene. Visual effects like explosions, smoke, or particle effects are added. - Sound Design:
Background music, sound effects, and dialogue are synchronized with the animation. - Editing:
The final animation is refined, trimmed, and formatted for its intended platform, whether it’s a film, game, or advertisement.
Why Is the Animation Pipeline Important?
The animation pipeline serves as a roadmap for animators, helping to organize workflows and maintain consistency. By breaking the process into clear stages, teams can collaborate efficiently, identify potential issues early, and ensure that deadlines are met.
Understanding the pipeline is essential for anyone looking to create professional 3D animations. Whether working independently or as part of a team, mastering these stages will enable animators to bring their creative visions to life while navigating the technical complexities of 3D animation.
Tools and Software for 3D Animation
The tools and software used in 3D animation are essential for transforming creative ideas into lifelike animations. Whether you’re a beginner or a professional, selecting the right software can significantly impact your workflow and the quality of your output. Below is a breakdown of popular tools and software, along with tips for choosing the best one for your needs.

Popular 3D Animation Software
- Blender
- Overview: Blender is a free, open-source 3D creation suite that offers robust features for modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, and compositing.
- Best For: Beginners and indie creators due to its cost and extensive online community.
- Pros: Free, regular updates, versatile, large community support.
- Cons: Slight learning curve for new users.
- Autodesk Maya
- Overview: A professional-grade software widely used in the film and gaming industries for complex animations and realistic effects.
- Best For: Advanced users and studios working on high-end projects.
- Pros: Industry standard, powerful tools for animation and rigging.
- Cons: Expensive subscription cost.
- Cinema 4D
- Overview: A user-friendly software known for motion graphics, 3D modeling, and animation.
- Best For Artists focusing on motion design and quick workflows.
- Pros: Intuitive interface, excellent for beginners in motion graphics.
- Cons: Higher price point.
- 3ds Max
- Overview: A comprehensive 3D modeling and animation software ideal for architectural visualization, gaming, and films.
- Best For: Modelers and animators in game development and design visualization.
- Pros: Powerful modeling tools, and integration with CAD workflows.
- Cons: High cost, Windows-only.
- Houdini
- Overview: A node-based software specializing in procedural generation and visual effects.
- Best For: Advanced animators and VFX artists.
- Pros: Procedural workflows, excellent for complex simulations.
- Cons: Steeper learning curve.
- Unreal Engine
- Overview: A real-time 3D creation tool often used for creating interactive animations and immersive environments.
- Best For: Real-time rendering, virtual production, and game animation.
- Pros: Free for many use cases, real-time feedback, photorealistic rendering.
- Cons: Requires powerful hardware.
- ZBrush
- Overview: A digital sculpting software used for creating highly detailed 3D models.
- Best For: Character and creature design.
- Pros: Exceptional sculpting tools, detail-oriented workflow.
- Cons: Limited in animation capabilities.
Criteria for Choosing the Right Software
- Skill Level: Beginners may prefer intuitive tools like Blender or Cinema 4D, while professionals may opt for Autodesk Maya or Houdini.
- Project Requirements: Select software that caters to your project’s focus, such as modeling, animation, or rendering.
- Budget: Blender is free, while tools like Maya and 3ds Max require paid subscriptions.
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure your computer meets the software’s hardware requirements.
Additional Tools to Enhance 3D Animation
- Adobe After Effects
- Use for: Compositing and adding post-production effects to animations.
- Substance Painter
- Use for: Texturing and material creation for 3D models.
- Unity
- Use for: Interactive animations and real-time rendering.
- Krita
- Use for: Creating digital storyboards and concept art.
By choosing the right combination of software and tools, animators can create professional-quality animations, streamline their workflow, and bring their creative visions to life. Remember to experiment with trial versions and explore online tutorials to find the software that best aligns with your goals and projects.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to make 3D animation?
Creating 3D animation involves a series of carefully planned steps, blending artistic vision with technical expertise. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate the process and bring your ideas to life:

1. Concept Development
This is the foundation of your animation project, where you establish the storyline and visual style.
- Generate Ideas: Brainstorm themes and narratives.
- Write a Script: Outline dialogue, key events, and scene transitions.
- Create a Storyboard: Sketch rough visuals to map out scenes, camera angles, and movements.
2. Creating 3D Models
Build the digital objects and characters that will populate your animation.
- Modeling: Use tools like Blender or Maya to sculpt 3D shapes for characters, props, and environments.
- Topology: Ensure clean geometry for efficient animation and rendering.
- Detailing: Add intricate features like facial expressions, folds in fabric, or texture-ready surfaces.
3. Texturing and Materials
Add color, texture, and materials to give your 3D models a realistic or stylized look.
- UV Mapping: Unwrap the 3D model into a flat surface to apply textures accurately.
- Texture Creation: Use tools like Substance Painter or Photoshop to design custom textures.
- Material Application: Define how surfaces reflect light (e.g., shiny, matte, metallic).
4. Rigging
Prepare your models for movement by adding a skeleton and controls.
- Add Bones: Create a digital skeleton within the model.
- Set Up Joints: Place joints at points of articulation, such as elbows or knees.
- Skinning: Bind the 3D model to the rig to ensure smooth deformations during animation.
5. Animation
Bring your characters and objects to life through motion.
- Keyframing: Set key poses at specific points in time, and the software interpolates movements in between.
- Timeline: Organize animations chronologically and adjust the timing for a natural flow.
- Secondary Motion: Add subtle movements like hair sway or cloth flutter for realism.
6. Lighting and Rendering
Set the mood and produce the final visual output.
- Lighting: Use virtual lights to create depth and highlight elements in your scene. Experiment with different types of lighting, such as ambient, directional, or spotlights.
- Rendering Settings: Adjust quality, resolution, and rendering techniques (e.g., ray tracing or real-time rendering).
- Test Renders: Render small sections to check for errors before committing to the full animation.
7. Compositing and Post-Production
Combine all elements and refine the final output.
- Layer Integration: Combine background, foreground, effects, and characters.
- Special Effects: Add particles, explosions, or other visual enhancements.
- Sound Design: Sync dialogue, background music, and sound effects to your animation.
Tips for Success
- Start Small: Begin with short projects to master the basics.
- Plan Rigorously: Detailed storyboards and pre-production can save time later.
- Leverage Tutorials: Learn techniques from online resources to improve your skills.
- Optimize Workflow: Use efficient rendering techniques and software shortcuts.
By following these steps, you’ll have a clear roadmap to create stunning 3D animations. Each stage requires practice and patience, but with dedication, you’ll be able to bring your imagination to life and create animations that captivate audiences.
Tips for Beginners in 3D Animation
Diving into 3D animation can feel overwhelming, but with the right approach and mindset, you can steadily build your skills and confidence. Here are some practical tips to help beginners navigate the world of 3D animation:

1. Start Small
- Focus on short, simple projects like animating a bouncing ball or a walking cycle.
- Avoid complex characters or elaborate scenes at the beginning; start with basic shapes and concepts.
2. Choose the Right Software
- Begin with beginner-friendly software like Blender (free and open-source).
- Experiment with trial versions of professional tools such as Autodesk Maya or Cinema 4D to explore advanced features.
3. Learn the Basics First
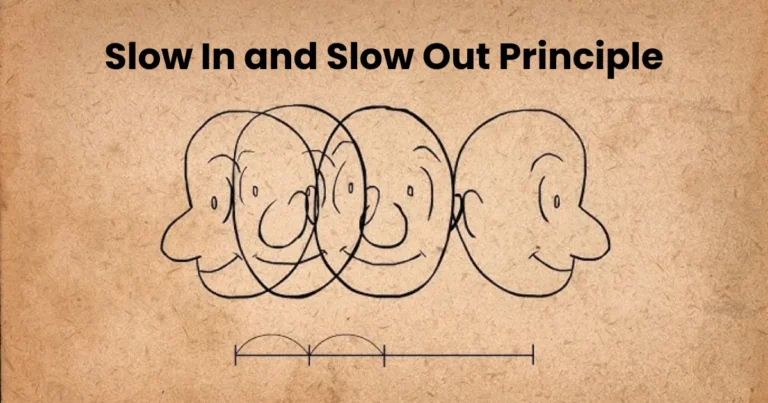
- Understand the Principles of Animation: Familiarize yourself with the 12 principles of animation, such as squash and stretch, timing, and anticipation.
- Study 3D Fundamentals: Grasp key concepts like modeling, rigging, texturing, and lighting.
4. Follow Online Tutorials and Courses
- Utilize free resources on platforms like YouTube, Blender Guru, or FlippedNormals.
- Invest in structured courses from websites like Udemy, Coursera, or Skillshare for more in-depth learning.
5. Practice Regularly
- Consistency is key in mastering 3D animation. Dedicate time each day or week to hone your skills.
- Experiment with different tools and techniques to expand your capabilities.
6. Observe Real-World Motion
- Pay attention to how people, animals, and objects move in real life.
- Use video references to study and replicate natural motion in your animations.
7. Join Communities
- Participate in online forums and communities like Blender Artists, CGSociety, or Reddit’s r/3Dmodeling.
- Share your work, seek feedback, and learn from other animators.
8. Don’t Be Afraid to Fail
- Mistakes are part of the learning process. Use them as opportunities to improve.
- Revisit old projects to see how much you’ve grown over time.
9. Optimize Your Workflow
- Learn keyboard shortcuts to save time and improve efficiency.
- Organize your files, models, and assets to make your projects manageable.
10. Explore Animation Challenges
- Participate in animation challenges or contests to practice and showcase your skills.
- These events can provide motivation and help you meet deadlines.
Challenges in 3D Animation and How to Overcome Them
3D animation is a rewarding but complex process that presents several challenges to beginners and professionals alike. From technical hurdles to creative struggles, understanding these challenges and learning how to overcome them is essential for a smooth workflow. Here’s a look at some common issues and practical solutions:

1. Steep Learning Curve
Challenge: 3D animation involves mastering a range of software and technical concepts, which can be intimidating for newcomers.
Solution:
- Start with beginner-friendly tools like Blender, which has an extensive library of tutorials.
- Break the process into smaller steps, focusing on one skill (e.g., modeling) before moving to the next.
- Follow structured courses and tutorials to learn at a manageable pace.
2. Time-Consuming Process
Challenge: Creating 3D animations can take a long time, especially during rendering or when perfecting intricate details.
Solution:
- Use low-poly models and simplified scenes for practice projects to speed up workflow.
- Optimize rendering by lowering the resolution or using real-time rendering tools like Unreal Engine for certain projects.
- Plan meticulously during the pre-production phase to reduce unnecessary revisions.
3. Hardware Limitations
Challenge: High-quality 3D animation requires powerful hardware, and working with limited resources can slow down your progress.
Solution:
- Invest in upgrades for key components like RAM, graphics cards (GPU), and storage.
- Use cloud-based rendering services to handle complex scenes.
- Learn optimization techniques, such as reducing polygon counts or using proxy models during animation.
4. Creative Blocks
Challenge: Animators may struggle to develop unique ideas or overcome creative stagnation.
Solution:
- Watch animated movies, play games, or explore online art galleries for inspiration.
- Take breaks and engage in other creative activities to refresh your mind.
- Collaborate with others or seek feedback to generate new perspectives.
5. Balancing Realism and Stylization
Challenge: Striking the right balance between realistic motion and artistic expression can be tricky.
Solution:
- Study the 12 principles of animation to understand how to exaggerate movements while maintaining believability.
- Use video references to guide realistic animations and blend them with your style.
- Experiment with stylized render settings to achieve a unique look.
6. Technical Glitches and Errors
Challenge: Software crashes, corrupted files, and bugs can disrupt workflow and cause frustration.
Solution:
- Save your work frequently and create multiple backups.
- Update your software regularly to fix bugs and access new features.
- Join online forums to seek advice and solutions for technical issues.
7. Managing Complex Scenes
Challenge: Large scenes with many assets can become difficult to navigate and may slow down your software.
Solution:
- Organize assets into layers or groups for easier management.
- Use proxies or low-resolution versions of models while working on the animation.
- Optimize lighting and effects to reduce rendering strain.
8. Meeting Deadlines
Challenge: Projects with tight deadlines can lead to stress and rushed results.
Solution:
- Use project management tools to plan tasks and set realistic goals.
- Break down the pipeline into smaller milestones to track progress.
- Learn to prioritize key elements and simplify less important aspects if time is limited.
9. Keeping Up with Industry Trends
Challenge: The 3D animation industry evolves rapidly, with new tools and techniques emerging frequently.
Solution:
- Stay updated by following blogs, forums, and YouTube channels dedicated to 3D animation.
- Attend workshops, webinars, or industry events to network and learn from peers.
- Experiment with emerging tools like AI-assisted animation to stay ahead.
While 3D animation comes with its share of challenges, each hurdle provides an opportunity to grow and refine your skills. By adopting a problem-solving mindset, leveraging resources, and continuously learning, you can navigate these challenges and create stunning animations that showcase your talent.
Applications of 3D Animation
3D animation is a versatile medium used across a wide range of industries. Its ability to create immersive visuals, realistic simulations, and engaging storytelling makes it an invaluable tool in various fields. Here are some of the most prominent applications of 3D animation:

1. Entertainment
- Film and Television: 3D animation is a cornerstone of the entertainment industry, powering blockbuster movies, animated series, and visual effects (VFX).
- Examples: Pixar’s animated films, and Marvel’s CGI-driven scenes.
- Video Games: Realistic characters, immersive environments, and dynamic actions in games rely heavily on 3D animation.
- Examples: Popular games like Fortnite or The Last of Us.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR experiences in games and films use 3D animation to transport users to fully immersive environments.
2. Marketing and Advertising
- 3D animated advertisements help brands create visually appealing and memorable campaigns.
- Product demos and explainer videos use 3D animation to showcase features and functions effectively.
- Example: A 3D animation of a car demonstrating safety features.
3. Architecture and Real Estate
- Architectural Visualization: 3D animation enables architects to create realistic walkthroughs of buildings and interiors before construction.
- Real Estate Marketing: Animated tours of properties allow potential buyers to explore spaces virtually.
4. Education and Training
- E-Learning: 3D animations simplify complex topics, making them engaging and easier to understand.
- Example: Visualizing molecular structures in biology.
- Professional Training: Simulations for fields like medical surgery, aviation, or engineering allow trainees to practice in a safe, controlled environment.
5. Healthcare and Medicine
- Medical Visualization: 3D animation helps illustrate biological processes, surgical procedures, and medical devices.
- Example: Animations showing how a vaccine works inside the body.
- Patient Education: Doctors use animated videos to explain diagnoses and treatment plans to patients.
6. Manufacturing and Engineering
- Product Design: Engineers use 3D animation to visualize and test prototypes before physical production.
- Industrial Training: Animated simulations teach workers how to operate machinery safely.
- Process Visualization: Animations demonstrate complex manufacturing processes for stakeholders.
7. Science and Research
- Simulations: Scientists use 3D animation to simulate phenomena like weather patterns, space exploration, or molecular interactions.
- Data Visualization: 3D graphics make abstract data easier to understand and analyze.
8. Retail and E-Commerce
- Product Configurators: Online tools with 3D models allow customers to customize products like furniture or vehicles.
- Virtual Try-Ons: Retailers use 3D animation for augmented reality (AR) features that let customers visualize how products like clothing or glasses will look on them.
9. Automotive and Aerospace Industries
- Vehicle Prototyping: 3D animation helps visualize new designs and test aerodynamics.
- Marketing: Automakers use 3D animations to showcase vehicles in advertisements.
- Simulations: Pilots and drivers train using 3D-animated simulators.
10. Social Media and Content Creation
- Animated 3D characters and short clips captivate audiences on platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok.
- Influencers and brands use 3D visuals to create standout content.
Future Applications
The potential of 3D animation is expanding with advancements in technology like artificial intelligence, virtual production, and real-time rendering. From augmented reality shopping experiences to virtual tourism, 3D animation continues to evolve and redefine its applications in daily life.
By adapting 3D animation to various needs, industries can enhance creativity, improve efficiency, and deliver engaging experiences to audiences worldwide.
Conclusion
Although 3D animation is a powerful medium that merges creativity, technology, and storytelling to produce engaging and impactful visual content it is always asked how to make 3D animation. From the entertainment industry to education, healthcare, marketing, and beyond, its applications are vast and transformative. The journey of creating 3D animations—starting from concept development, modeling, and rigging to rendering and post-production—requires skill, patience, and persistence.
For beginners, the world of 3D animation may seem daunting, but with the right tools, consistent practice, and a willingness to learn, it becomes a rewarding and enjoyable process. The challenges faced along the way, such as mastering complex software or managing hardware limitations, are part of the growth and refinement that leads to success.
The evolution of 3D animation is driven by advancements in technology like artificial intelligence, real-time rendering, and virtual reality. As these tools become more accessible, the scope of 3D animation continues to expand, offering exciting opportunities for professionals and hobbyists alike.
Whether you’re creating breathtaking visual effects for a blockbuster movie, designing immersive educational tools, or exploring the possibilities of virtual reality, 3D animation is a versatile and ever-evolving art form. By embracing its challenges and opportunities, animators can push the boundaries of creativity and leave a lasting impact on audiences across the globe.
The future of 3D animation is limitless, and for those passionate about bringing ideas to life, the journey is as inspiring as the destination.