State-of-the-Art Image Segmentation Models
Contents
In the fast-evolving field of computer vision, state-of-the-art image segmentation models have transformed how machines interpret and process visual data. These advanced models accurately separate objects from backgrounds, enabling precise analysis across various industries. With deep learning techniques improving rapidly, researchers continue to develop more efficient and accurate segmentation architectures. This article explores the latest state-of-the-art image segmentation models, their types, key techniques, and wide-ranging applications. Moreover, we will discuss the challenges these models face and the promising trends shaping their future. By understanding these models, you can appreciate their role in advancing computer vision and artificial intelligence.
What Are State-of-the-Art Image Segmentation Models?
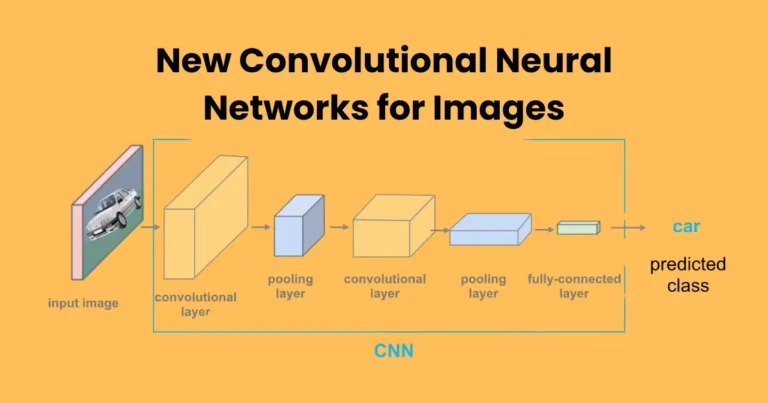
State-of-the-art image segmentation models are advanced deep learning architectures designed to partition an image into meaningful regions, making it easier for machines to identify and interpret visual data. Unlike traditional methods, these models leverage sophisticated algorithms and neural networks to achieve high precision and efficiency.
These models classify each pixel of an image into a specific category, which helps distinguish objects, backgrounds, and finer details. As a result, these are crucial for tasks requiring precise visual understanding, such as medical imaging, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
What truly sets these models apart is their ability to generalize across diverse datasets while maintaining exceptional accuracy. Techniques like convolutional neural networks (CNNs), fully convolutional networks (FCNs), and transformer-based architectures drive their performance. Thanks to these innovations, state-of-the-art image segmentation models continue to push the boundaries of computer vision and artificial intelligence.
Types of Image Segmentation
State-of-the-art image segmentation models are designed to handle different tasks, depending on the level of detail and complexity required. Let’s explore the three primary types of image segmentation:

1. Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation assigns a label to every pixel in an image, classifying them into specific categories. However, it does not differentiate between multiple objects of the same type. For instance, in an image of a street, all cars would be labeled as “car” without distinguishing between individual vehicles. State-of-the-art image segmentation models like DeepLab and Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs) excel at this task, offering high accuracy and efficient performance.
2. Instance Segmentation
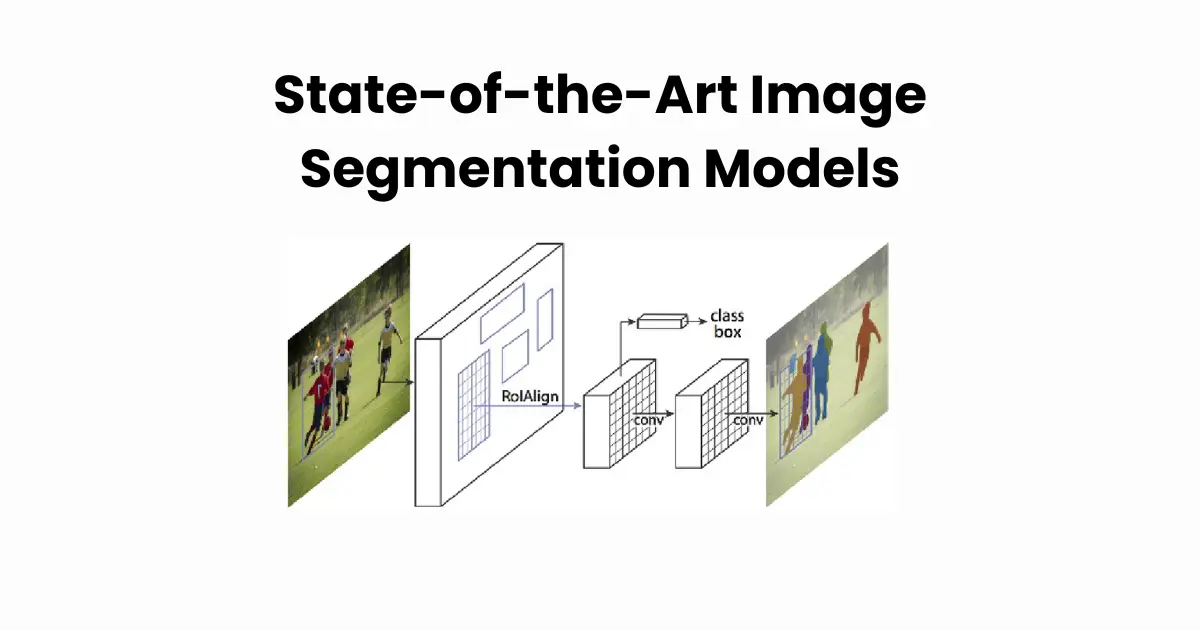
Unlike semantic segmentation, instance segmentation identifies individual objects within the same category. Every object is treated as a separate entity, even if they belong to the same class. For example, each car in a street scene would be uniquely labeled. Models like Mask R-CNN have become the gold standard for this type of segmentation due to their ability to precisely detect and outline individual instances.
3. Panoptic Segmentation
Panoptic segmentation combines the strengths of semantic and instance segmentation. It assigns a class label to every pixel while also distinguishing between different instances of the same object. This approach provides a complete understanding of the scene, making it ideal for complex visual tasks. State-of-the-art image segmentation models like Panoptic FPN and DETR (DEtection TRansformer) have pushed the boundaries of this method, delivering remarkable results in accuracy and efficiency.
Each type of segmentation serves a unique purpose, and choosing the right approach depends on the specific requirements of the task. By leveraging these advanced techniques, state-of-the-art image segmentation models continue to revolutionize computer vision applications.
Key Techniques Used in State-of-the-Art Image Segmentation Models
State-of-the-art image segmentation models leverage advanced deep learning techniques to achieve high accuracy and efficiency. These techniques enhance the ability of machines to analyze images at a pixel level, enabling precise segmentation. Below are some of the most effective techniques used in modern segmentation models:

1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs are the foundation of most state-of-the-art image segmentation models. They use convolutional layers to extract spatial features from images, allowing models to detect patterns such as edges, shapes, and textures. By stacking multiple layers, CNNs create deep feature hierarchies, making them highly effective for pixel-wise classification in segmentation tasks.
2. Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs)
FCNs improve upon traditional CNNs by replacing fully connected layers with convolutional layers, enabling the model to make dense predictions for every pixel in an image. This structure allows FCNs to handle images of varying sizes while preserving spatial information, making them a key component of modern segmentation architectures.
3. U-Net Architecture
Originally designed for medical image segmentation, U-Net has become one of the most widely used architectures in image segmentation. It follows an encoder-decoder structure, where the encoder extracts high-level features while the decoder refines spatial details. Skip connections between corresponding encoder and decoder layers help recover fine-grained details, improving segmentation accuracy.
4. Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN extends Faster R-CNN by adding a segmentation branch to generate pixel-wise masks for detected objects. It excels in instance segmentation, where multiple objects of the same class need to be separated. By combining object detection and segmentation, Mask R-CNN delivers high precision in real-world applications such as autonomous driving and medical imaging.
5. DeepLab Models
DeepLab models, including DeepLabV3 and DeepLabV3+, use dilated (atrous) convolutions to increase the receptive field of CNNs without losing spatial resolution. Additionally, they incorporate spatial pyramid pooling to capture multi-scale contextual information, enhancing the segmentation of complex scenes. These improvements make DeepLab models among the best choices for semantic segmentation tasks.
Each of these techniques contributes to the success of state-of-the-art image segmentation models, enabling them to achieve exceptional performance across various applications. By leveraging deep learning advancements, these models continue to push the boundaries of computer vision and artificial intelligence.
Applications of Image Segmentation Models
State-of-the-art image segmentation models have found widespread applications across numerous industries, transforming how machines interpret and analyze visual data. Their ability to provide detailed, pixel-level classification makes them indispensable for tasks requiring high accuracy and efficiency. Let’s explore some of the most impactful applications:

1. Medical Imaging
Image segmentation plays a crucial role in medical diagnostics and treatment planning. By segmenting organs, tissues, and abnormalities from medical scans like MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays, doctors can detect diseases at an early stage. State-of-the-art image segmentation models like U-Net offer exceptional precision, aiding in tasks like tumor detection, organ delineation, and surgical planning.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
For self-driving cars, understanding the surrounding environment is essential. Image segmentation models help these vehicles identify and differentiate between roads, pedestrians, vehicles, traffic signs, and obstacles.
3. Satellite Image Analysis
Satellite imagery requires high-resolution segmentation for applications like urban planning, agriculture monitoring, and environmental analysis. Image segmentation models distinguish between land types, water bodies, and vegetation, providing critical data for decision-making. This technology helps track deforestation, monitor crop health, and assess disaster impacts with unparalleled detail.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
In AR and VR environments, accurate segmentation of real-world objects enhances user interaction and immersion. Image segmentation models help identify and track objects, enabling realistic overlays and interactive experiences. For example, AR applications can place virtual objects in real-world spaces by understanding the boundaries and shapes of physical objects.
5. Industrial Inspection
Quality control in manufacturing often relies on automated visual inspection systems. Image segmentation models detect surface defects, misalignments, and anomalies in products with high accuracy. This automation reduces the need for manual inspection, increasing efficiency and ensuring consistent product quality.
These diverse applications highlight the transformative potential of state-of-the-art image segmentation models. By offering detailed and accurate visual interpretation, these models continue to advance technologies across healthcare, transportation, environmental monitoring, and beyond.
Challenges in Image Segmentation
Despite the impressive capabilities of state-of-the-art image segmentation models, they face several challenges that affect their accuracy, efficiency, and real-world applicability. Overcoming these obstacles requires innovative approaches and continuous research. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most significant challenges:

1. Computational Complexity
State-of-the-art image segmentation models often require significant computational resources. High-resolution images and complex architectures demand powerful GPUs and large memory capacities. As a result, deploying these models on devices with limited resources, like mobile phones or embedded systems, becomes difficult.
2. Limited Training Data
For accurate segmentation, models need diverse and well-annotated datasets. However, collecting and labeling high-quality training data is time-consuming and expensive. In fields like medical imaging, data scarcity becomes even more pronounced, as expert knowledge is required for precise annotations. This lack of data often limits the generalization capabilities of image segmentation models.
3. Model Generalization
A state-of-the-art image segmentation model trained on a specific dataset may struggle when applied to new environments or data types. Variations in lighting, angles, and object appearances can lead to performance drops. Achieving robust generalization across different datasets remains a key challenge in computer vision.
4. Boundary Precision
Accurately segmenting objects with fine or irregular boundaries is another difficult task. Models often produce blurred or imprecise edges, especially when objects are closely packed or have similar textures. Techniques like atrous convolutions and attention mechanisms help mitigate this issue, but perfect boundary delineation remains a work in progress.
5. Real-Time Performance
Many applications, like autonomous driving and augmented reality, require real-time segmentation. However, the heavy computational load of state-of-the-art image segmentation models can lead to latency issues. Balancing speed and accuracy without sacrificing performance is a persistent challenge for researchers and developers.
Addressing these challenges is essential for enhancing the efficiency and practicality of state-of-the-art image segmentation models. As research continues, innovations in architecture, data augmentation, and optimization techniques will help overcome these obstacles, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in computer vision.
Future Trends in State-of-the-Art Image Segmentation Models
The evolution of state-of-the-art image segmentation models continues at a rapid pace, driven by breakthroughs in deep learning and computer vision. As the demand for higher accuracy and efficiency grows, several promising trends are shaping the future of this field. Let’s explore some of the most significant developments:

1. Transformer-Based Architectures
Transformers, initially designed for natural language processing, are making waves in computer vision. Models like Vision Transformers (ViTs) and Segmenter are being adapted for image segmentation, offering exceptional performance by capturing long-range dependencies and global context. Their ability to handle complex visual tasks with high accuracy positions them as a key trend for future advancements.
2. Self-Supervised Learning
One of the biggest challenges in image segmentation is the need for large, labeled datasets. Self-supervised learning addresses this by enabling models to learn useful features from unlabeled data. Techniques like contrastive learning and masked image modeling are helping state-of-the-art image segmentation models generalize better while reducing dependency on annotated datasets.
3. Real-Time Segmentation
Real-time performance is crucial for applications like autonomous driving and augmented reality. Future models are focusing on lightweight architectures and efficient inference techniques to balance speed and accuracy. Optimizations like model pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation are expected to drive faster and more efficient segmentation systems.
4. Multi-Modal Learning
Combining visual data with other modalities like text, depth, or LiDAR can enhance segmentation performance. Multi-modal models leverage diverse information sources to improve object recognition and context understanding. This trend is particularly important for robotics, autonomous systems, and medical imaging.
5. Generative Models for Data Augmentation
Data scarcity remains a bottleneck for training robust segmentation models. Generative models like GANs and diffusion models are being used to create synthetic, high-quality datasets. By generating diverse and realistic training samples, these models help improve the generalization and performance of state-of-the-art image segmentation models.
As these trends continue to evolve, state-of-the-art image segmentation models will become even more powerful, efficient, and versatile. The future promises enhanced real-time capabilities, better generalization, and the ability to tackle increasingly complex visual tasks with unprecedented precision.
Conclusion
State-of-the-art image segmentation models have revolutionized the field of computer vision by providing exceptional accuracy and efficiency in identifying and classifying objects at the pixel level. These advanced models, powered by techniques like convolutional neural networks, fully convolutional networks, and transformer-based architectures, offer precise and detailed visual understanding across various applications.
From medical imaging and autonomous vehicles to augmented reality and industrial inspection, the real-world impact of these models is undeniable. Despite their impressive capabilities, challenges like computational complexity, data limitations, and real-time performance constraints still need to be addressed. However, continuous research and innovation promise to push these boundaries even further.
As the demand for high-quality visual interpretation grows, state-of-the-art image segmentation models will remain at the forefront of technological advancement, shaping the future of artificial intelligence and computer vision.